The Secret World of Capybara Social Dynamics
Dive into the fascinating realm of capybaras, the world's largest rodents, and uncover the intricate social structures that govern their lives. From their complex hierarchies to their unique bonding behaviors, these gentle giants of South America have much to teach us about cooperation and community in the animal kingdom.
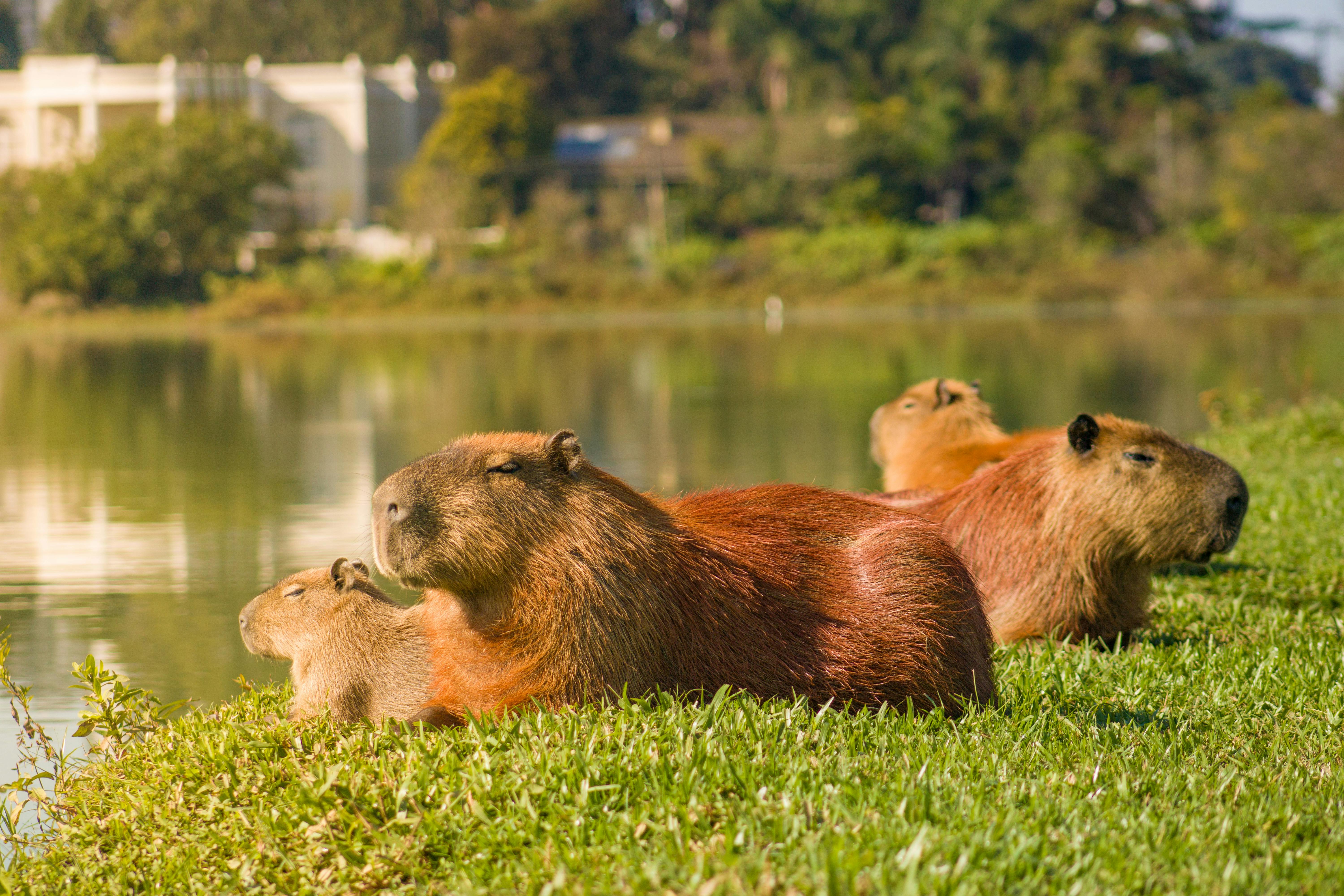

The Basics of Capybara Society
Capybaras are highly social creatures, living in groups that can range from 10 to 100 individuals. These groups, often called herds, are not random assemblages of animals but carefully structured societies with distinct roles and hierarchies. At the core of each herd is a dominant male, who leads the group and maintains order. Surrounding him are females, their offspring, and subordinate males. This structure provides safety, efficiency in foraging, and better chances of survival for the entire group.
Hierarchical Harmony
The social hierarchy within capybara herds is not static but dynamic, with constant subtle shifts in status. Dominant males must regularly assert their position through displays of strength and aggression, while younger males may challenge for leadership. Females also have their own hierarchy, often based on age and reproductive status. This complex system ensures that resources are distributed effectively and that the group functions as a cohesive unit.
Communication is Key
Capybaras have developed a rich vocabulary of vocalizations and body language to communicate within their herds. From high-pitched whistles that signal danger to low grunts used in friendly interactions, these rodents have a nuanced system of communication. They also use scent marking extensively, with specialized glands that allow them to leave chemical messages for other capybaras. This sophisticated communication network helps maintain social bonds and coordinate group activities.
Cooperative Child-Rearing
One of the most fascinating aspects of capybara social dynamics is their approach to raising young. In a behavior known as alloparental care, adult capybaras will often care for young that are not their own. This cooperative breeding strategy ensures that pups have the best chance of survival, with multiple adults watching over them and even nursing them. This level of cooperation is rare in the animal kingdom and speaks to the highly evolved social nature of capybaras.
The Role of Play in Social Development
Play is not just for fun in capybara society; it serves a crucial role in developing social skills and establishing hierarchies. Young capybaras engage in mock fights, chases, and other playful behaviors that help them learn the rules of their society. These play sessions also allow young capybaras to form bonds with their peers, which can last throughout their lives and contribute to the overall cohesion of the herd.
Adaptations to Human Presence
As human populations expand into capybara habitats, these adaptable animals have shown remarkable flexibility in their social structures. In some urban areas, capybaras have formed smaller groups and adjusted their behaviors to coexist with humans. This ability to modify their social dynamics in response to environmental changes demonstrates the intelligence and resilience of these remarkable rodents.
The Economic Impact of Capybara Social Behavior
The unique social behavior of capybaras has not gone unnoticed by the tourism industry. In recent years, there has been a growing trend of capybara-watching tours in countries like Brazil and Venezuela. These tours, which allow visitors to observe capybara herds in their natural habitats, have become increasingly popular among wildlife enthusiasts. The estimated price range for such tours can vary widely, from $50 to $500 per person, depending on the duration and location. This emerging ecotourism niche has the potential to contribute significantly to local economies while promoting conservation efforts for capybara habitats.
Lessons from Capybara Society
Studying capybara social dynamics offers valuable insights into the evolution of social behavior in mammals. Their cooperative breeding, complex communication systems, and adaptable social structures provide a unique model for understanding how animals navigate group living. As we face our own social challenges in human society, perhaps we can draw inspiration from these peaceful and cooperative creatures.
The Future of Capybara Research
As our understanding of capybara social dynamics grows, so too does the potential for new discoveries. Researchers are now exploring the cognitive abilities of capybaras, investigating their problem-solving skills and emotional intelligence. Future studies may reveal even more surprising aspects of their social lives, potentially changing our perceptions of rodent intelligence and social complexity.
The secret world of capybara social dynamics is a testament to the intricate and fascinating social lives that exist in the animal kingdom. From their hierarchical structure to their cooperative child-rearing, capybaras demonstrate a level of social sophistication that challenges our understanding of animal societies. As we continue to study and appreciate these remarkable creatures, we not only gain insights into the natural world but also find new ways to reflect on our own social structures and behaviors.